Tube Ice Machine for Sale: Efficient Commercial Ice Makers
Strategic Investment: The Value Proposition of Tube Ice Machines in Industrial Applications
In diverse industrial sectors ranging from food processing and chemical manufacturing to large-scale concrete cooling, the demand for efficient, high-quality ice production is paramount. A reliable tube ice machine for sale represents a critical capital investment designed to meet these stringent requirements. This article delves into the technical intricacies, market dynamics, and operational advantages of tube ice technology, providing decision-makers and engineers with comprehensive insights to inform their procurement strategies.
Industry Trends and Market Dynamics
The global industrial ice machine market is experiencing consistent growth, driven by expanding manufacturing capabilities, increasing food safety regulations, and a heightened focus on energy efficiency. Projections indicate a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) exceeding 5% for industrial ice production equipment over the next five years, with significant demand stemming from Asia-Pacific and North America. This growth is underpinned by the versatility of tube ice, which is favored for its slow melting rate, large contact surface, and robust structure, making it ideal for a multitude of industrial cooling applications. Key trends include the integration of advanced automation (PLC control), adoption of eco-friendly refrigerants (e.g., R507A, Ammonia), and a shift towards modular, scalable designs that facilitate easier installation and maintenance. The market also increasingly values suppliers offering comprehensive after-sales support and custom engineering solutions.
Understanding Tube Ice Technology: The Manufacturing Process
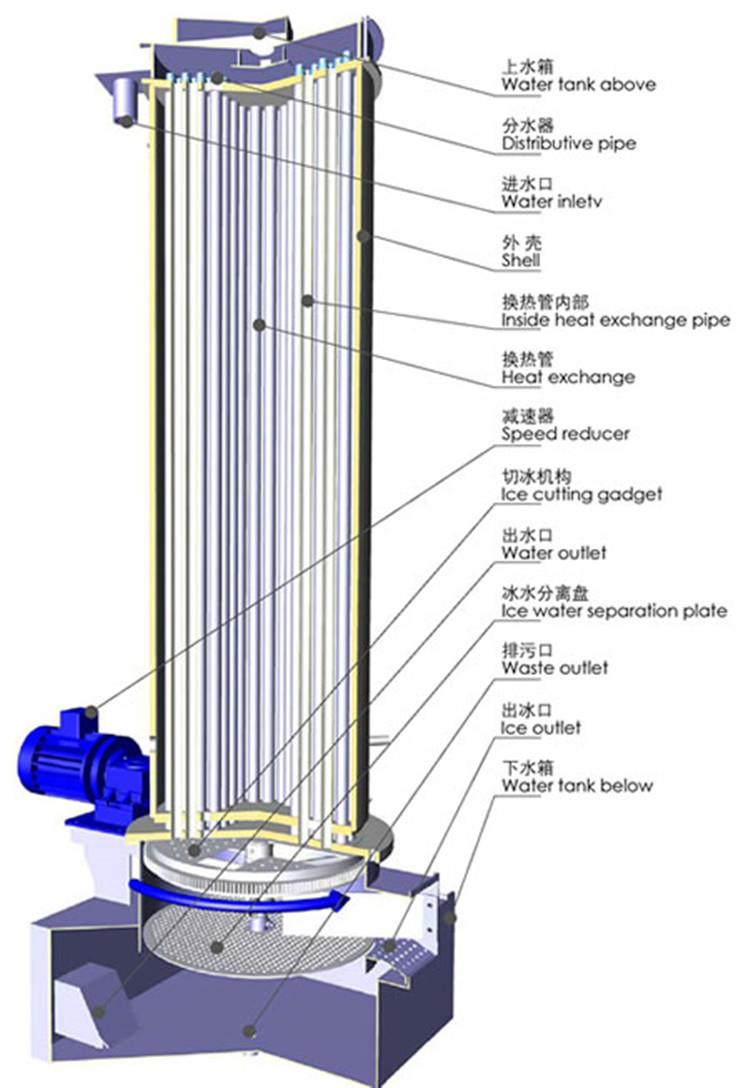
The production of tube ice involves a sophisticated, continuous refrigeration cycle designed for optimal efficiency and ice purity. Understanding this process is crucial for evaluating any tube ice machine for sale.
Detailed Process Flow:
- Water Supply and Pre-treatment: Potable water, often pre-filtered or softened to remove impurities and minerals, is supplied to the water distribution tank. This pre-treatment is vital for producing clear, hard ice and extending the service life of the machine’s components by minimizing scale build-up.
- Refrigeration Cycle Initiation: The core of the system is a robust refrigeration unit, typically utilizing a high-efficiency screw or reciprocating compressor. The refrigerant (e.g., Ammonia, R404A, R507A) is compressed, condensed in an evaporative or air-cooled condenser, and then expanded through a throttle valve, leading to a significant temperature drop.
- Ice Formation in the Evaporator: The super-cooled refrigerant circulates within the jacket of the vertical tube evaporator. Water from the distribution tank is continuously pumped upwards and flows downwards along the inner surface of the evaporator tubes. As the water passes over the cold surfaces, it gradually freezes, forming cylindrical ice layers within the tubes. The unique vertical design ensures efficient heat exchange and uniform ice growth.
- Hot Gas Harvest (Defrost): Once the ice tubes reach the desired thickness, a pre-programmed hot gas defrost cycle is initiated. Hot refrigerant gas from the compressor bypasses the condenser and is directed into the evaporator jacket. This causes a slight warming of the tube surfaces, allowing the ice tubes to detach and fall under gravity into an ice cutter.
- Ice Cutting and Discharge: The fallen ice tubes are then precisely cut into uniform lengths (typically 28mm, 34mm, or 40mm in diameter, and 25-50mm in length) by a rotating cutter blade. The cut tube ice is then discharged into an insulated storage bin or directly conveyed to its application point.
- Automated Control System: A Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) monitors and controls all aspects of the process, ensuring optimal performance, energy efficiency, and safety. This includes temperature regulation, water flow, ice thickness, and harvest cycles.
Materials, Manufacturing, and Quality Assurance
The durability and hygienic integrity of a tube ice making machine are intrinsically linked to its construction materials and manufacturing processes. High-quality evaporators are typically constructed from food-grade stainless steel (SUS304 or SUS316) to ensure corrosion resistance and compliance with stringent hygiene standards, such as those stipulated by ISO 22000 (Food Safety Management). Components like compressors, condensers, and expansion valves are sourced from reputable international brands known for their reliability and performance.
Manufacturing processes involve precision CNC machining for critical components to ensure tight tolerances, advanced automated welding techniques for leak-proof and robust connections, and meticulous assembly. Each commercial tube ice machine undergoes rigorous factory acceptance testing (FAT) to verify performance parameters, energy consumption, and structural integrity. Adherence to international testing standards like ISO 9001 for quality management and ANSI/ASME for pressure vessels is non-negotiable, ensuring a service life often exceeding 15-20 years with proper maintenance.
A high-capacity tube ice machine for sale, engineered for industrial demands.
Target Industries and Application Advantages
Tube ice machines find extensive applications across various demanding sectors:
- Petrochemical and Chemical Industry: Used for cooling chemical reactions, solvent recovery, and temperature control in exothermic processes. Advantages include controlled cooling rates and chemical compatibility with specific materials.
- Metallurgy and Mining: Employed in processes requiring rapid cooling of materials or machinery. The robust nature of tube ice resists rapid melting, providing sustained cooling.
- Food Processing and Fisheries: Essential for preserving seafood, meat, poultry, and fresh produce. The hollow structure allows for a larger cooling surface area, rapid temperature reduction, and resistance to caking. Compliance with FDA standards for ice used in direct food contact is critical.
- Concrete Cooling: Large quantities of tube ice are used to lower the temperature of concrete mixes, particularly in mass concrete pours for dams, bridges, and high-rise buildings. This prevents thermal cracking, improves workability, and enhances the final strength of the concrete.
- Water Supply & Drainage / Environmental Engineering: Used for effluent cooling, wastewater treatment processes, and maintaining consistent temperatures in water treatment plants.
In these scenarios, the inherent advantages of tube ice — particularly its energy-saving profile due to efficient heat transfer and its excellent corrosion resistance from stainless steel components — significantly contribute to operational efficiency and cost reduction over the machine's extended service life.
Key Technical Specifications and Performance Parameters
When considering a tube ice machine for sale, a thorough review of technical specifications is paramount. These parameters dictate the machine's suitability for specific industrial demands, its operational costs, and overall reliability.
Typical Product Specification Table
| Parameter | Description/Value Range |
|---|---|
| Ice Production Capacity | 5 TPD to 100 TPD (Tons Per Day), customizable up to 200+ TPD |
| Ice Diameter & Length | Standard: Ø28mm, Ø34mm, Ø40mm; Length: 25-50mm (adjustable) |
| Refrigerant Type | R404A, R507A, R717 (Ammonia) - selected based on capacity and regulations |
| Compressor Type | Hermetic/Semi-hermetic Reciprocating or Screw Compressors (e.g., Bitzer, Mycom, Hanbell) |
| Evaporator Material | Food-grade Stainless Steel SUS304 or SUS316L |
| Condenser Type | Air-cooled, Water-cooled, or Evaporative Condenser |
| Power Supply | 3 Phase, 380V/50Hz, 400V/50Hz, 440V/60Hz (customizable) |
| Operating Temperature | Ambient: 5°C to 40°C; Water Inlet: 0.5°C to 30°C |
| Control System | Fully Automatic PLC Control (Siemens, Schneider, Mitsubishi) with HMI interface |
| Cooling Capacity Efficiency (COP) | Typically 3.5 - 4.5 (kW/kW), depending on ambient conditions and refrigerant |
| Ice Outlet Temperature | Approximately -5°C to -8°C |
These specifications highlight the robust engineering behind a high-performance tube ice making machine. The choice of refrigerant significantly impacts environmental footprint and operational safety; Ammonia (R717) systems, while requiring stringent safety protocols, offer superior thermodynamic efficiency for larger installations. PLC control systems provide not only automation but also remote monitoring capabilities, fault diagnosis, and data logging, critical for predictive maintenance and optimizing operational costs. The selection of the condenser type (air, water, or evaporative) depends heavily on local climate, water availability, and energy cost considerations, directly impacting the overall efficiency of the commercial tube ice machine.
Application Scenarios and Industry Impact
The versatility of tube ice makes it an indispensable component in numerous industrial processes, directly influencing product quality, process efficiency, and cost management. Its unique cylindrical shape with a hollow core facilitates faster cooling and prevents clumping, a critical advantage over other ice forms.
Diverse Applications of a Tube Ice Machine for Sale:
- Concrete Cooling: Large-scale construction projects, especially in hot climates, rely on tube ice to control the exothermic reaction of cement hydration. Adding ice directly to the concrete mix lowers its temperature, preventing thermal cracks and improving long-term structural integrity. This application demands high volumes of consistently produced ice, a strength of any robust tube ice making machine.
- Chemical and Pharmaceutical Industries: Temperature control is vital for many chemical reactions, preventing unwanted side reactions, ensuring product stability, and managing exothermic processes. Tube ice provides a reliable and precise cooling medium, often in jacketed reactors or directly within mixing processes. Its purity is critical in pharmaceutical manufacturing, where contamination can have severe consequences.
- Food Processing and Beverage Production: From chilling poultry and seafood to mixing dough in bakeries and rapid cooling of beverages, tube ice plays a crucial role in maintaining product freshness and inhibiting bacterial growth. Its slow melting rate helps preserve freshness during transportation and storage, enhancing food safety and extending shelf life.
- Fishing and Seafood Preservation: Immediately after catch, tube ice is used to chill fish and seafood, significantly reducing spoilage. The ice can be easily stored, transported, and distributed on fishing vessels or at processing plants, ensuring the catch arrives at market in optimal condition.
- Logistics and Cold Chain Management: Tube ice is an excellent solution for maintaining precise temperatures in refrigerated trucks, containers, and warehouses, especially for perishable goods where continuous, uniform cooling is essential.
- Environmental Remediation: In certain environmental engineering applications, ice can be used for temperature management in biological treatment processes or for ground freezing techniques.
The impact of a well-selected commercial tube ice machine extends beyond mere cooling. It contributes to regulatory compliance (e.g., HACCP for food safety), reduces waste through better preservation, and improves the overall quality and marketability of end products.
Technical Advantages and Operational Efficiency
Investing in a modern tube ice machine for sale offers a myriad of technical advantages that directly translate into operational efficiencies and significant cost savings over its lifecycle.
Core Advantages:
- Superior Energy Efficiency: Contemporary tube ice machines are engineered with advanced refrigeration components (e.g., high-COP compressors, optimized evaporators, efficient heat exchangers) that minimize electricity consumption. The direct expansion system in the evaporator provides excellent heat transfer, reducing the energy required per ton of ice produced. Specific energy consumption can be as low as 60-70 kWh/ton for larger ammonia systems, significantly lower than many other ice types.
- Durability and Reliability: Constructed from robust materials like SUS304 or SUS316 stainless steel for water-contact parts, these machines are highly resistant to corrosion and wear. Key components from internationally recognized manufacturers ensure a long operational lifespan and minimize downtime. Regular maintenance, as per manufacturer guidelines, extends this lifespan further.
- Automated Operation and Low Maintenance: Fully automated PLC control systems (e.g., Siemens, Mitsubishi) allow for seamless operation with minimal human intervention. Features like automatic water replenishment, ice harvesting, and safety shutdowns enhance reliability. The simple and robust design, fewer moving parts compared to flake ice machines, and accessibility of components contribute to lower maintenance requirements and costs.
- High Ice Quality and Consistency: Tube ice is characterized by its hardness, clarity, and slow melting rate. The hollow cylindrical shape increases the surface area for cooling while preventing rapid melting and caking, which is crucial for applications requiring sustained cooling. Its purity levels often exceed drinking water standards, making it safe for direct contact with food and in sensitive chemical processes.
- Environmental Responsibility: Many modern commercial tube ice machine models can operate with natural refrigerants like Ammonia (R717), which has zero Ozone Depletion Potential (ODP) and Global Warming Potential (GWP), aligning with increasing environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals.
These technical advantages translate into a compelling economic case for businesses. Reduced energy bills, lower maintenance expenses, and consistent production of high-quality ice contribute directly to a stronger ROI and enhanced operational competitiveness.
Vendor Comparison and Selection Criteria
Choosing the right provider for a tube ice machine for sale is a strategic decision that extends beyond initial purchase price. It involves evaluating a vendor's technical capabilities, manufacturing quality, customization options, and long-term support.
Key Considerations for Vendor Selection:
- Experience and Reputation: Look for vendors with a proven track record (e.g., decades of experience) in manufacturing industrial refrigeration equipment. Review customer testimonials and case studies.
- Certifications and Compliance: Ensure the manufacturer adheres to international quality standards such as ISO 9001, CE for European markets, and local pressure vessel codes. Food-grade certifications (e.g., HACCP, FDA-compliant materials) are essential for food processing applications.
- Component Quality: Inquire about the brands of compressors, refrigerants, and control systems used. Reputable components from global leaders like Bitzer, Mycom, Siemens, or Danfoss indicate a commitment to quality and reliability.
- Customization Capabilities: Assess the vendor's ability to tailor machines to specific requirements, including unusual capacities, specific ice dimensions, integration with existing cooling systems, or unique environmental conditions.
- After-Sales Support and Service Network: Critical for operational continuity. Evaluate the availability of spare parts, technical support, on-site assistance, and training programs. A strong global or regional service network is a significant advantage.
- Energy Efficiency Data: Request documented energy consumption figures (kWh/ton of ice) under various operating conditions and compare them across vendors. This directly impacts operational expenditure.
Comparative Overview (Illustrative)
| Feature | Vendor A (e.g., Global Leader) | Vendor B (e.g., Regional Specialist) | Vendor C (e.g., Cost-Effective) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Typical Capacity Range | 10 TPD - 200+ TPD | 5 TPD - 80 TPD | 3 TPD - 50 TPD |
| Energy Consumption (kWh/ton) | 60-75 (Ammonia), 80-95 (Freon) | 70-85 (Ammonia), 90-105 (Freon) | 95-120 (Freon only) |
| Evaporator Material | SUS316L Standard | SUS304 Standard, SUS316L Optional | SUS304 Standard |
| Control System | Advanced PLC with Remote Monitoring | Standard PLC with HMI | Basic PLC with Manual Override |
| After-Sales Support | Global Network, 24/7 Support | Regional Support, Business Hours | Limited Online Support |
| Customization Options | Extensive, Turnkey Solutions | Moderate Customization | Minimal Customization |
This table illustrates how different vendors may position their tube ice making machine offerings. While cost-effective options might seem appealing, the long-term total cost of ownership (TCO) often favors higher-quality, more efficient machines with robust support, especially for mission-critical industrial applications.
Customized Solutions and System Integration
In industrial settings, a one-size-fits-all approach rarely suffices. Leading manufacturers offering a tube ice machine for sale understand the necessity of providing tailored solutions that integrate seamlessly into existing plant infrastructure and specific operational workflows.
Customization options can include:
- Capacity Scalability: Designing modular systems that allow for future expansion of ice production capacity without extensive overhauls.
- Refrigerant Choice: Selection between Freon (HFCs like R404A, R507A) or Ammonia (R717) based on local regulations, energy efficiency targets, and safety considerations.
- Ice Delivery Systems: Integration with automated ice storage bins, screw conveyors, pneumatic ice delivery systems, or ice pumps to efficiently transport ice directly to consumption points.
- Water Pre-treatment: Custom water filtration, softening, or reverse osmosis (RO) systems to ensure optimal water quality for ice production, especially in regions with hard water or specific purity requirements (e.g., FDA standards for potable ice).
- Control System Features: Advanced PLC programming for integration with existing SCADA systems, remote diagnostic capabilities, energy management modules, and customized HMI interfaces for specific operational data display.
- Ambient Conditions Adaptability: Designing units to operate efficiently in extreme ambient temperatures, from arid desert environments to humid tropical regions. This may involve specialized condensers or insulation.
Effective system integration ensures that the commercial tube ice machine operates as a cohesive part of a larger industrial process, maximizing efficiency and minimizing potential bottlenecks. Collaborative design and engineering between the client and manufacturer are key to successful implementation, yielding a highly optimized and reliable ice production solution.
Real-World Application Case Studies
The practical benefits of a high-quality tube ice machine for sale are best illustrated through real-world applications, showcasing improved efficiency, cost savings, and enhanced product quality.
-
Case Study 1: Large-Scale Concrete Batching Plant, Middle East
Challenge: A major construction company operating in a hot desert climate faced significant challenges with concrete cracking and rapid setting due to high ambient temperatures. They required a continuous supply of over 80 TPD of ice to cool their concrete mix, ensuring structural integrity for a large infrastructure project.
Solution: Two 40 TPD tube ice making machine units with evaporative condensers and an integrated automated ice storage and delivery system were installed. The machines utilized R717 (Ammonia) for maximum energy efficiency, given the large capacity requirement.
Outcome: The system provided a consistent, reliable supply of -5°C tube ice, effectively lowering the concrete mix temperature by an average of 10°C. This resulted in a significant reduction in thermal cracking, improved workability, and adherence to stringent project specifications, leading to timely project completion and enhanced structural quality. Operational costs were kept low due to the high energy efficiency of the Ammonia-based system.
-
Case Study 2: Seafood Processing Facility, Southeast Asia
Challenge: A large seafood exporter needed to rapidly chill and maintain the freshness of various fish and shrimp species immediately after harvest and during processing. Traditional ice methods led to inconsistent cooling and higher spoilage rates, impacting product quality and market value. They required a hygienic, continuous ice supply of 20 TPD.
Solution: A custom-designed 20 TPD commercial tube ice machine, built with SUS316L stainless steel for all water contact surfaces to meet strict HACCP and FDA food safety standards, was installed. The machine used R404A refrigerant and featured an integrated water pre-treatment system.
Outcome: The facility achieved rapid and uniform chilling of seafood, significantly extending shelf life and reducing bacterial growth. The hard, slow-melting tube ice minimized product damage during handling. This directly led to a 15% reduction in post-harvest losses and a noticeable improvement in product quality, enhancing the company's reputation and export capabilities.
These examples underscore the critical role of specialized tube ice making machine solutions in addressing specific industrial challenges and driving operational excellence.
Ensuring Trust: FAQs, Warranty, and Support
Trustworthiness in B2B transactions hinges on transparency, clear commitments, and robust after-sales support. When procuring a tube ice machine for sale, these elements are crucial.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
Q1: What are the primary factors influencing ice production capacity?
A: Key factors include ambient temperature, inlet water temperature, and the specific model's refrigeration power. Higher ambient and water temperatures will slightly reduce nominal capacity. -
Q2: Is the ice produced safe for food contact?
A: Absolutely. Our machines use food-grade stainless steel (SUS304/316L) for all water-contact surfaces, and the production process is designed for optimal hygiene. We adhere to international food safety standards (e.g., HACCP, ISO 22000). Proper water treatment is also crucial for purity. -
Q3: What kind of maintenance is required for a tube ice machine?
A: Regular maintenance includes checking refrigerant levels, cleaning the condenser and evaporator, inspecting electrical connections, and ensuring water quality. A detailed maintenance schedule is provided with each machine. -
Q4: Can the ice machine operate continuously?
A: Yes, our industrial tube ice making machine models are designed for 24/7 continuous operation. The PLC control system manages all cycles automatically to ensure consistent production. -
Q5: What is the estimated lead time for a new machine?
A: Lead times vary based on capacity and customization. Standard models typically require 6-8 weeks for manufacturing and testing, followed by shipping. Custom solutions may extend this to 10-14 weeks. Specific timelines are provided upon order confirmation.
Lead Time and Fulfillment
Efficient project management and transparent communication are central to our fulfillment process. Upon order confirmation for a commercial tube ice machine, a detailed production schedule is provided. This includes milestones for material procurement, manufacturing, quality control, pre-shipment inspections, and logistics. We leverage robust supply chain networks and streamlined manufacturing processes to ensure timely delivery without compromising on quality. Expedited options may be available for urgent projects, subject to discussion.
Warranty Commitments
All our tube ice making machine units come with a standard 12-month warranty from the date of commissioning or 18 months from shipment, whichever comes first. This warranty covers manufacturing defects and component failures under normal operating conditions. Extended warranty options and comprehensive service contracts are available for enhanced peace of mind, offering coverage for up to 5 years on major components like compressors and evaporators. Our warranty terms are clearly articulated in every sales agreement.
Customer Support and After-Sales Service
Our commitment to clients extends far beyond the initial purchase. We offer comprehensive after-sales support designed to maximize the uptime and efficiency of your tube ice machine for sale. This includes:
- Technical Assistance: 24/7 remote technical support via phone, email, and video conferencing.
- Spare Parts Availability: A readily available inventory of genuine spare parts and components to minimize repair times.
- On-site Service: Skilled technicians available for installation supervision, commissioning, troubleshooting, and major repairs globally.
- Training Programs: Comprehensive training for your operational and maintenance staff to ensure proficient handling of the equipment.
- Preventative Maintenance Programs: Tailored service agreements to ensure your machine operates at peak efficiency throughout its lifespan.
Our dedication to supporting our clients reinforces our position as a trusted partner in industrial ice production.
Conclusion
The decision to acquire a tube ice machine for sale is a strategic investment that profoundly impacts operational efficiency, product quality, and long-term cost-effectiveness across a multitude of industrial sectors. From its meticulously engineered manufacturing process and robust technical specifications to its versatile application scenarios and inherent energy-saving advantages, the modern tube ice machine stands as a testament to advanced refrigeration technology. By prioritizing factors such as vendor reputation, material quality, customization capabilities, and comprehensive after-sales support, businesses can ensure they procure a solution that not only meets their immediate demands but also provides sustained value and reliability for decades to come. As industries continue to evolve, the demand for high-performance, sustainable ice production solutions will only intensify, solidifying the critical role of these essential machines.
References
- International Institute of Refrigeration. (2020). *Guide to Refrigeration Technology and Applications*. IIR Publishing.
- ASHRAE Handbook - Refrigeration. (2022). *Chapter 48: Ice Manufacture*. American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers.
- Food and Drug Administration (FDA). (2019). *Current Good Manufacturing Practices (CGMP) Regulations for Food and Beverages*. Code of Federal Regulations, Title 21.
- ISO 9001:2015. (2015). *Quality management systems — Requirements*. International Organization for Standardization.
- Li, Z., & Chen, G. (2018). *Thermal and Hydraulic Performance of Ice Machines*. Journal of Refrigeration, 42(3), 154-167.






